HL7 Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) is a structured format for exchanging clinical data. A producer of information (a content creator) follows a series of rules (called templates) to construct an XML document which can be displayed or semantically interpreted by a recipient (or a content consumer). CDA is based in an early version of the HL7v3 standard, and shares many terms and concepts with HL7 Version 3.
A CDA document is logically structured as illustrated in Figure 1, and consists of four major types of elements.
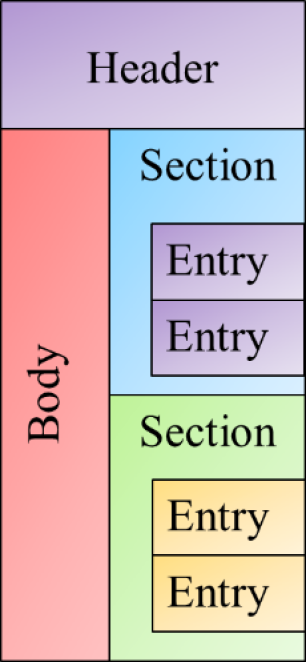
 Figure 1 - Logical View of a CDA Document
Figure 1 - Logical View of a CDA Document
- Header: Which contains data related to the document such as the subject (patient whose data is represented within the body), author, data enterer, custodian (original location of data), etc.
- Body: Which contains the content of the document. This content can be structured (as a structuredBody) or unstructured (as a nonXmlBody)
- Sections: Which represent major organizations of data such as advance directives, problems, allergies, medications, etc. These sections may or may not contain discrete data elements, however they must contain text which can be used by consumers to render content which they cannot semantically interpret.
- Entries: Which represent either a single data point (such as an observation, procedure, encounter, etc.) or logical grouping of data points (such as a battery, or medication regimen).
Additionally, CDA consists of three levels of conformance which describes the level of detail or semantic data contained within the document, they are as follows:
- Level 1: A level 1 CDA document consists of a structured header and an unstructured body. A Level 1 CDA document may convey PDF, RTF, HTML or proprietary other content which cannot be encoded by the content creator.
- Level 2: A level 2 CDA document consists of a structured header, and a structured body having codified sections. Sections carry a textual representation of the clinical data stored in the content creator classified by a code.
- Level 3: A level 3 CDA document consists of a structured header, a structured body having codified sections which are comprised of discrete data contained within entries. These entries contain data which can be semantically understood by the recipient of the document.
Level 3 is represents an extension of a Level 2 document and they are often interchangeable. For example, a consumer which only understands CDA at Level 2 (section import) can store a Level 3 document, conversely a consumer which implements Level 3 (discrete import) can still interpret a Level 2 document. Additionally some document templates will represent a mixture of level 2 and level 3 content, or may give the implementer a choice of using a level 2 section or a codified level 3 section.


Figure 1 - Logical View of a CDA Document