This is page is a work in progress. This info bubble will be removed once the TWG feels it is complete. |
This page presents real world integration experiences that the team has collated. This information serves as background to help others understand some of the values and workflows created by this TWG.

Bidirectional OpenMRS ↔ CommCare Integration
Dimagi built a point-to-point connection between CommCare and OpenMRS using the existing APIs. OpenMRS is the source of truth for this integration. The workflow focuses on exporting a list of people for community follow-up and entering them in to CommCare. Information collected in CommCare gets sent to OpenMRS as encounters and observations. CommCare is not responsible for creating new patients as part of this workflow.
Setup:
- Map CommCare form to the appropriate OpenMRS entity (Patient, Encounter, Visit, Observation, Person)
- Build orchestration workflow
- Activate atom feed
Generic Steps for CommCare Central System → OpenMRS:
- User collects a form in the mobile app
- Mobile app syncs to the central system
- Central system identifies that there is a form that needs to go to the third party system
- Each different type of CommCare form has a different action.
- Additionally, the state of the case.xml vs the OpenMRS patient is considered at each integration point
- Central system queries OpenMRS to verify state
- Does the patient exist
- What's the latest record
- Central system compares the OpenMRS state against the current state
- If no difference, then they stop the workflow here
- Central system orchestrates the multistep process of creating entities in OpenMRS
- Create a patient if it doesn't exist (this also creates a person)
- Start a visit
- Create an encounter
- Create observations
- End the visit (within a 24 hour period)
- Store appropriate duplicate information in CommCare case.xml for that patient
- Central system closes out the connection and marks it as done.
Generic Steps for OpenMRS → CommCare Central System:
- CommCare queries the OpenMRS atom feed for each entity type (patient, encounter, observation) on a regular schedule
- CommCare loops through each item in the atom feed and queries the OpenMRS system
- CommCare identifies the changes, runs through logic and applies the changes locally
- Create cases for new patients
- Create form submissions for new encounters
- Update case properties in the event OpenMRS has the latest information
- CommCare marks the atom feed item as processed and saves state on each entry
Additional Notes:
- These transactions need to be rolled back if there's a failure partially through
- We need to identify which system should win in the event that there's a conflict
- We replay the event submissions across both systems in the order they were received because the state of a single variable or observation may have changed multiple times and the last one in generally wins.
- Users often duplicate properties so they can see everything in one place instead of overriding properties generated in their system. So, they would add "openmrs_" properties to each case so it's clear the latest version of a field from OpenMRS
Referral Workflow
Referrals are when a patient is referred from a community to a central health facility or visa versa so that they can receive care that that team can provide. Referrals are a package of information sent from the CHIS to the EMR in this instance.
Generic Steps:
- User collects a form in the mobile app
- Mobile app syncs to the central system
- Central system identifies that there is a referral that needs to go to the third party system
- Central system creates the referral package by mapping incoming form submission fields to the output(s)
- Central system sends the package(s) to the third party system
- Note: This may require creating multiple entities in the third party system and the Central data repository is responsible for orchestrating that. For example, you first need to create the patient, then the encounter, then the observations with the ability to roll back changes.
- Third party system receives the package and confirms that it was received
- Third party system parses each package and stores them in the system
- Third party system may trigger internal events based on this changing information
CommCare and DHIS2 Anonymous Events
CommCare ---> DHIS2
CommCare Form -> DHIS2 Anonymous Event
Workflow
- A mobile worker submits a form to the central server
- Data is mapped from CommCare form question values to DHIS2 data elements, event date, org unit (location) and program. (30 kinds of forms, half a dozen indicators per form.)
- A single payload is pushed to DHIS2
Project summary
An application integrates the entire Ministry of Health’s curriculum (elementary multipurpose agents curriculum) into one platform. The platform collects real time data entered by CHWs who deliver health services in the remote areas where they live. Dimagi, with the collaboration of the partner, developed a live integration of every form submissions using the anonymous events functionality into the Ministry of Health DHIS2 instance.
CommCare and DHIS2 DataSets
CommCare ---> DHIS2
CommCare Report -> DHIS2 DataSet
Workflow
- Mobile workers submit many forms over a period of a month
- After the start of the next month, CommCare retrieves a report for the month just completed. (The report has one column per category option per data element. e.g if the "Live Births" data element is broken down by two gender category options and three attendee category options, the report will have 2 x 3 = 6 columns for live births.)
- Report data is mapped to data elements and category options, and submitted for the period of the month just completed.
Project Summary
Dimagi has collaborated with the partner and Ministry of Public Health to develop the integration between the CommCare application used at the community level and the DHIS2 instance setup by the Ministry. Using MOTECH and the aggregated integration feature, monthly aggregated reporting data coming from community health workers is sent to the DHIS2 instance of the Ministry of Health. The scope of the application includes all indicators on the monthly activity report covering data for IMCI, Surveillance and also stock management.
CommCare and OpenMRS (with Reports)
CommCare <--> OpenMRS
CommCare Case <- OpenMRS Report
CommCare Case + Form -> OpenMRS Patient + Observations
Workflow: CommCare <--- OpenMRS
- Once a week CommCare retrieves a report from OpenMRS using its Reporting API.
- Report columns are mapped to case properties
- Cases are created or updated (based on whether their "external_id" property already exists) and mapped case property values are set.
Workflow: CommCare ---> OpenMRS
- A mobile worker submits a form
- CommCare form questions and case properties are mapped to OpenMRS Patient properties, Visit properties, Encounter properties and Observations.
- OpenMRS patients are never created, because all CommCare cases have been imported from OpenMRS
- A workflow of requests to the OpenMRS API is followed:
- Update identifiers
- Update "preferred name"
- Update "preferred address"
- Update other standard properties
- Update custom attributes
- Create Visit
- Create Encounter
- Create Observations
- The original state is stored until the workflow is complete, and a failed API call will roll back the workflow by reversing the requests.
- The OpenMRS server is selected based on the location of the mobile worker.
Project Summary
In order to automate workflows, Dimagi has supported the partner to develop a two-way integration between OpenMRS and a CommCare application. This integration pulls data once a week from multiple OpenMRS instances into a single CommCare instance and has successfully allowed health facilities to replace what was previously a manual effort conducted by the team. As part of this collaboration, Dimagi has also trained the local project team in how to configure and maintain this integration so that they can independently and sustain this beyond Dimagi’s involvement in the project.
Fully automated 2-way integration between the CommCare app and OpenMRS, removing any manual work involved, in at least one health facility of each one of the partners of the consortium.
Multi-instance setup where one CommCare instance exchanges data with several OpenMRS instances. This was dictated by the implementation model adopted in which each health facility has its own OpenMRS instance.
Once a week CommCare pulls patients that meet the program participation criteria from all active OpenMRS instances.
Upon submission of a visit form a Visit, an Encounter and several Observations are created in OpenMRS, according to the location of the user, ensuring that the information collected is reflected in OpenMRS. Patient demographics are also updated in OpenMRS if they change.
CommCare and OpenMRS (with Atom feed)
CommCare <--> OpenMRS
CommCare Case + Form <--> OpenMRS Patient + Observations
CommCare Case <- OpenMRS Atom feed
Workflow: CommCare <--> OpenMRS
- A mobile worker submits a form
- CommCare form questions and case properties are mapped to OpenMRS Patient properties, Visit properties, Encounter properties and Observations.
- OpenMRS Patients are searched and matched with CommCare cases. If no definitive match is found, a new Patient is created.
- The Patient's system-generated ID (as opposed to national ID or facility ID) is saved to the CommCare case as unique, indexed "external ID".
- The standard OpenMRS workflow is followed
- The OpenMRS server is selected based on the location of the mobile worker.
Workflow: CommCare <--- OpenMRS
- CommCare polls the OpenMRS Patient, and Encounter Atom feeds. Atom feeds list the IDs of new and modified Patients and Encounters.
- CommCare fetches an OpenMRS Patient details, matches the Patient with a case on CommCare external ID, and creates a new case if one is not found.
- New CommCare cases are assigned to a supervisor for the facility's location, who will allocate cases to mobile workers.
- Case properties are set from values from Patients and the Observations of Encounters.
NOTE: CommCare form submissions can create OpenMRS Observations, but the reverse is not true: Observations set CommCare case property values; they do not submit forms of a CommCare app.)
Project Summary
Dimagi supported the single and bi-directional integration between the CommCare app and their OpenMRS / Bahmni system. This integration allowed for data tracked in the hospital management system to stay in-step with data collected by clinicians in the facilities. Dimagi also built capacity within the local project team to maintain and extend the CommCare application as well as the integration component of their system.
CommCare beneficiaries are exported to OpenMRS (and Bahmni, the hospital management system built on top of OpenMRS) based on their location. When cases are updated, their OpenMRS records are updated too.
CommCare beneficiaries are created/updated when a clinician at a facility updates a corresponding patient, so that a CHW can follow up. Updates from the CHW are sent back to the clinic/OpenMRS.
CommCare and OpenClinica
CommCare <--> OpenClinica
Workflow: CommCare <--- OpenClinica
- A CommCare app is generated from an OpenClinica Study Definition
Workflow: CommCare ---> OpenClinica
- At the conclusion of a clinical study, a pre-defined report is exported to OpenClinica over an API in CDISC format
Unidirectional OpenSRP → OpenMRS Integration
OpenSRP is responsible for sending data to OpenMRS in a number of implementations. The primary use case is to exchange health worker information from the local OpenSRP facility based app to a central instance of OpenMRS. This workflow is the same as identified in the Bidirectional OpenMRS → CommCare Integration above.
Bidirectional OpenSRP ↔ RapidPro Integration
OpenSRP has a deep point-to-point integration with RapdiPro in a couple implementations so that users can submit data via SMS to create patients and collect health information in OpenSRP, OpenMRS and the dashboard.
The system consists of 4 main parts:
- The end user: The end user sends a message via a mobile device to an SMS short code. The short code is then received by RapidPro for processing.
- RapidPro: This is the system that received the SMS messages from the CHW and validates the information against the expected syntax. It also manages the SMS flow and performs relevant validation checks before forwarding to the Canopy system.
- Canopy: This system converts and translates the coded messages based on the code card. The code card is a set of SMS syntax that the VHW references in order to send the required messages.It also forwards the data between the other connected systems. Canopy also contains the data warehouse, which the Analysis component depends on, and the Superset Dashboard, used to create and develop indicators that can be easily viewed and filtered. This set of systems consists of data tools that include RapidPro, NiFi, and Superset and PostgreSQL.
- OpenSRP (Health Data Store): This is where all the client and health related data is stored. This is a centralized server that will integrate the mobile app.
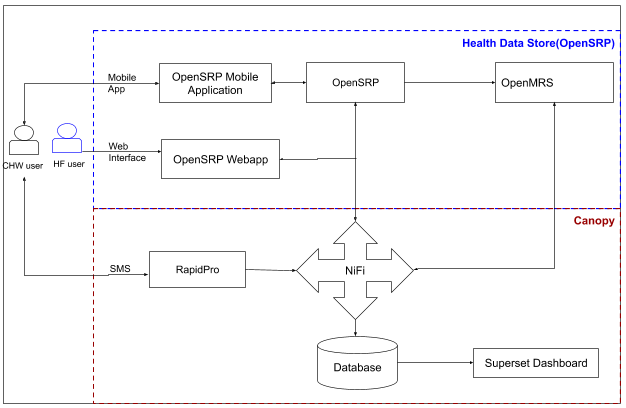
The diagram shows 2 categorizations of the system components, namely Canopy and OpenSRP (Health Data Store).
- Canopy is a set of solutions that provide robust data analytics for the data set. It is comprised of the below open systems
- RapidPro: A messaging agent that caters for communication via various social channels and SMS. RapidPro is the system that handles all SMS and chat API communications with the relevant logic to validate the content of the messages. It also handles contact information and minimal access control.
- NiFi: A mediation system that enables ETL functionality and workflow logic.
- Superset: A business intelligence and analytical tool that allows dynamic dashboards through an easy to use interface.
- Health Data Store is a set of systems that stores the health records.
- Web Dashboard: This is a web application that enables the data to be viewed by the end user. It has the logface, compartments, and analysis tab.
- OpenSRP CHW Application: This is a mobile app that can be used by the Village and Commune health workers.
- OpenSRP: A web server and lightweight EMR that stores and synchronizes data for the mobile app.
- OpenMRS: An heavyweight EMR solution, with a full user interface, that enables the use of data in a traditional EMR environment.
Bidirectional Referrals OpenSRP CHW App ↔ OpenSRP Facility Based App
Link: https://smartregister.atlassian.net/wiki/spaces/Documentation/pages/1156251738/FHIR+Task+Based+Referrals+Software+Requirements+Specification
Generic Steps:
- CHW decides that they need to refer a patient to a health facility
- The CHW opens the referral form for that patient, completes it and clicks save
- Post Save Action
- We generate a task in the CHW application
- The task is added to the referrals task list in the CHW app
- The CHW app automatically synchronizes 15 minutes
- The task and referral form are sent to the server and added to the queue of forms to download at that health facility
- The Facility app synchronizes and downloads the referral and task
- The task is added to the task list in the facility app
- A visual indicator also shows up next to patient in the appropriate register
- The user taps the task from the task list to open it
- The referral information is displayed and the user can navigate away or they can mark the referral as done
- Post Save Action
- The task status changes to Complete if the referral is marked as done
- Navigate Back Action
- The task has now been read, so we need to update the task status to "In Progress"
- The Facility app synchronizes after 15 minutes and updates the task in the server
- The CHW app synchronizes, identifies there is an updated task and updates the task locally to show the status as complete
CHT↔OpenMRS: Lost to Follow-Up (bidirectional)
Summary
For patients who missed important appointments at the health facility, CHWs need to proactively find them to encourage them to visit the health facility. Technically speaking, a report is generated in OpenMRS that contains a list of all the patients who need to be followed-up with. This report is sent to the CHT and for each patient on that list, a task is sent to CHWs requesting the CHW to find and refer the patient to the health facility.
Patient Process
- One time sync of all patients between the CHT server and OpenMRS
- When creating new patients in the CHT mobile app, CHWs have the opportunity to enter an EMR ID.
CHW syncs. - If the patient has an EMR ID, nothing is sent to OpenMRS*
- If the patient does not have an EMR ID, patient details are sent to OpenMRS and a person + patient is created. A unique identifier generated by the CHT is also stored in OpenMRS. NOTE: When patients are created in OpenMRS, they are not sent to the CHT
LTFU Process
- Report is run in OpenMRS which includes all the patients who need to be followed-up
- IL grabs report from OpenMRS and pushes to CHT server
- For each patient in the report, IL checks to see if they exist in the CHT. If not, create the patient in the CHT and allocate to a supervisor who will review and assign to the appropriate CHW.
- CHW syncs mobile app.
- CHW receives tasks for patients that need to be followed-up.
CHT↔KenyaEMR: COVID-19 Contact Tracing (bidirectional)
Summary
Suspected cases registered in the CHT are sent to OpenMRS. In OpenMRS, testing/lab results are obtained/recorded, as are additional contacts of cases. Confirmed cases and additional contacts are sent back to the CHT. Confirmed cases are advised and their contacts are followed-up for 10 days. If a contact becomes a suspected case, the cycle starts over.
Process
- Suspected COVID patient registered in CHT
- Sync mobile app, central server sends to OpenMRS
- CHT sends one payload, OpenMRS splits to person, patient, and case
- Patient visits clinic for testing, labs, etc..
- When labs are complete, if case is confirmed COVID, this confirmation and a list of additional contacts to trace are sent to the CHT central server
- CHT central server splits and allocates to appropriate tracers
- Tracers receive a task to follow-up with confirmed cases
- Tracers receive a task to follow-up with contacts of confirmed cases for 10 days or until the contact becomes a suspected case
- If a contact becomes a suspected case, start back at #1
CHT↔Bespoke EMR: Referrals (bidirectional)
Summary
CHWs do assessments for sick children using the CHT mobile app. If the CHT mobile app determines that the child should be referred to the health facility, the CHT server (once the CHW syncs) will send information about the patient and the referral to the facility based server. When patients arrive at the health facility, they will have access to information from the community. If the patient does not arrive at the health facility by the end of the next day, the facility based system will send a notification to the CHT central server indicating a ‘no show’. This generates a task for the CHW to follow-up with the patient and encourage them to visit the health facility. If the patient does visit the health facility, various results from the visit are sent back to the CHW to be delivered to the patient.
Process
- Patient registered in CHT mobile app
- Assessment done on patient
- If assessment results in a referral, once the CHW syncs to the central server, this referral gets sent to the facility based system
- Facility based system looks to see if the patient exists already (using an ID generated by the CHT), if not, creates this patient in the facility based system.
- Referral is added to patient
- When patient arrives, check-in clerk looks up patient in facility based system and has access to referral information from the CHW
- If after 24h the patient does not arrive, the facility based system sends a notification to the CHT central server and a task is created for the CHW to follow-up with the patient again
- Once the patient arrives in the health facility, various activities initiated by doctor or pharmacist can be sent back to the CHW
CHT→DHIS2: Aggregate dataSet reporting (unidirectional)
Summary
Monthly DHIS2 Aggregate reporting, one way (CHT to DHIS2). CHWs perform their normal duties throughout the month and can see their aggregate totals for each indicator on the DHIS2 dataSet. At the end of the month, they must sync to the central server. Supervisors sync to receive these aggregate totals from each CHW and the Supervisor’s app also aggregates across the entire DHIS2 orgUnit. Supervisors can all see each CHW’s contribution towards a given indicator. Once confirmed, a Health Records Information Officer can download a file from the CHT which is in the format required by DHIS2 and upload this file as a DHIS2 dataSet in their DHIS2 instance. More details and documentation here.
Process
- CHWs perform their normal duties throughout the month, viewing their aggregate data while offline in their app
- CHWs sync to central server
- Supervisor syncs to receive each CHWs aggregate totals
- Supervisor reviews totals across their catchment area
- HRIO downloads file from CHT central server and uploads to DHIS2
CHT↔RapidPro: Multiple use cases (bidirectional)
Summary
Multiple integrations with RapidPro have been developed and are live in several countries. Details of several RapidPro integration use cases can be found here.
Use Cases
- Client Initiated Health Assessments
- Contact Tracing
- Self quarantine
- Remote training
- CHW Symptom and Mental Health checks
