...
eHealth Framework
Domain Experts View
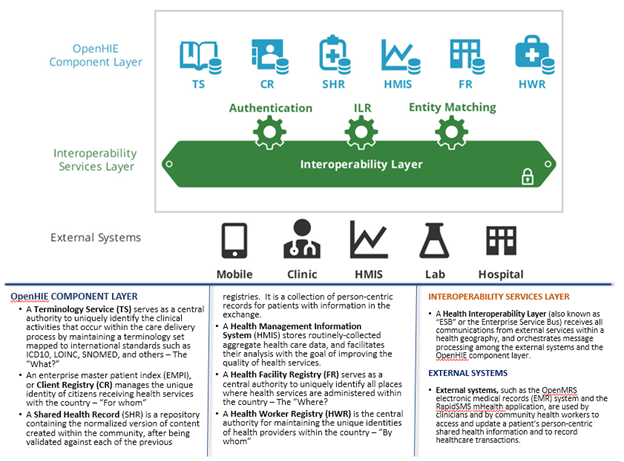
Figure: OpenHIE Architecture
The OpenHIE architectureIn the diagram above is depicted the building blocks of a Health Information Exchange based upon the the OpenHIE Architecture, namely: Client Registry, Facilities Registry, IOL Layer…
...
Health Management Information System, Health Worker Registry, Shared Health Record, and Terminology Services, and the Interoperability Services Layer that interconnects them all and provides Authentication, Interlinked Registries, and Entity Matching services.
The framework of components of HIE provides for integration with various standards compliant systems and tools, such as (but not limited to):
OpenMRS
DHIS2
Country and Partner EHRsIHE Profiles
PEPFAR DATIM
etc.
Developer's View
- Interface development
OpenHIM Mediators
- Working with standards
- Core Workflows (fit for purpose, standards compliant)
OpenHIE Assumptions
There are a few key assumptions that are made when considering OpenHIE. (( Help us build these out and write them out to why they are impactful and how to mitigate them ))
- Connectivity between Point of Care (PoC) and HIE: to leverage the full functionality of the OpenHIE a constant connection is preferable. Store and forward and asynchronous options are implementable and need to be discussed as to how to best leverage these
- ?Data Access?
- Record Modification?
- Error Management SOPs and workflows
...