The purpose of the Shared Health Record (SHR) software implementation is to provide a centralized repository for storing health data; with the goal of facilitating health information exchange among client systems. In line with the direction of the OpenHIE project, of which it this is a part of, the OpenSHR SHR does not aim to be a project-specific implementation of a Shared Health Record, but rather it aims to provide a framework and several core software components that can be used to implement a specific SHR.
This document will focus on the high-level architectural design for the OpenSHRSHR. Please refer to this document for the OpenSHR SHR requirements. The requirements themselves will be considered concluded within the scope of this document. For the Shared health Record component, we have decided to make use of OpenMRS as the core technology to built offon which to build a solution. The review process that we went through to make this decision is described in in the tool recommendation document. This design document will describe the modifications needed to allow OpenMRS to be used as a an SHR for OpenHIE.
To design a Shared health Health Record (SHR) around the OpenMRS platform, we will need to modify OpenMRS to be able to perform the functions of a an SHR. Some of the key changes that we will need to make are as follows:
- Support the storage of unstructured data eg, e.g. documents such as CDA level 1 - 3
- Remove the user interface so that the SHR can run as a headless service (separate the service layer from the UI layer)
- Add standards-based interfaces to interact with the SHR eg, e.g. add endpoints for XDS.b + CDA or profiled HL7v2
- Add mechanisms for processing, storing and querying structured and unstructured data within OpenMRS
- Add hooks at various stages of the data lifecycle life cycle for things like clinical decision support or data validation.
- Make sure everything can be mapped to as an encounter-based domain model
- Allow Investigate solutions for allowing the OpenMRS SHR to scale horizontally
- Modify the database for in order to optimize performance based on the SHR use case
- Modify required fields OpenMRS fields and data model constraints in order to suit a an SHR.
- Evaluate the encounter/obs tables against the ORUR01 schema, and discuss potential changes that will make our data model more hl7 compliant.
In the sections that follow we will explain these in more details detail and give a design of how these functions can be accomplished implemented within OpenMRS.
Overview
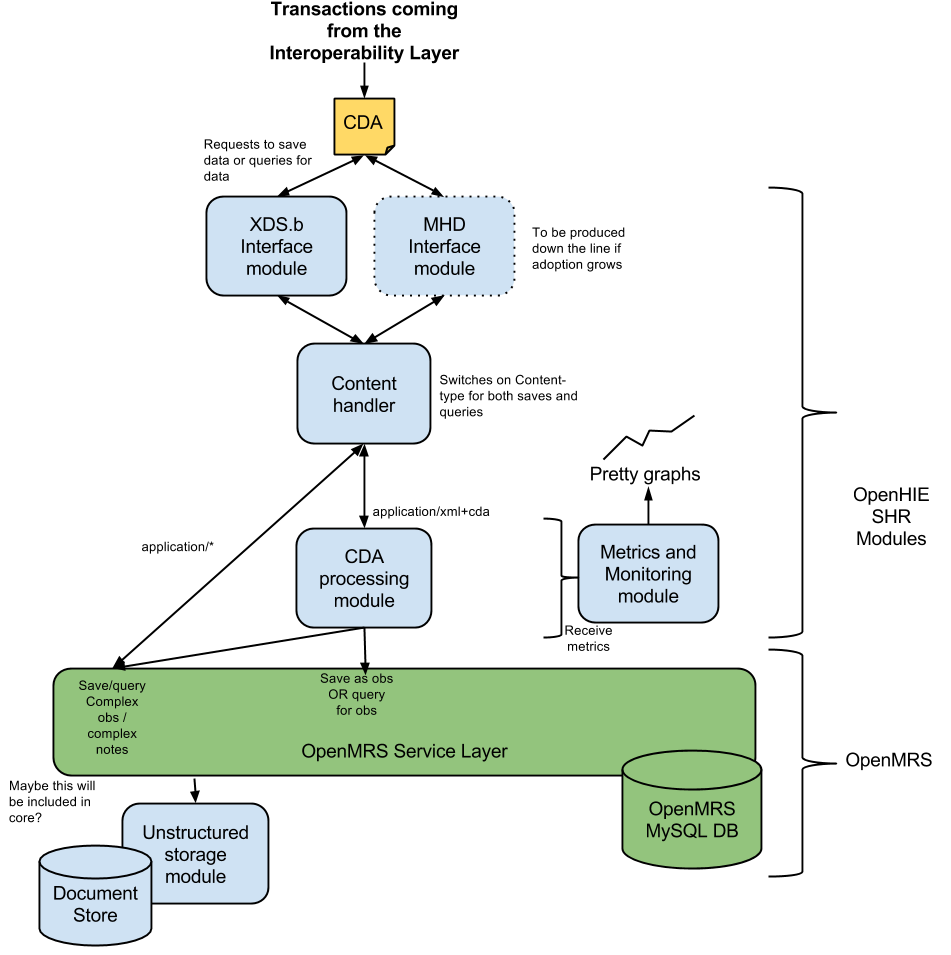
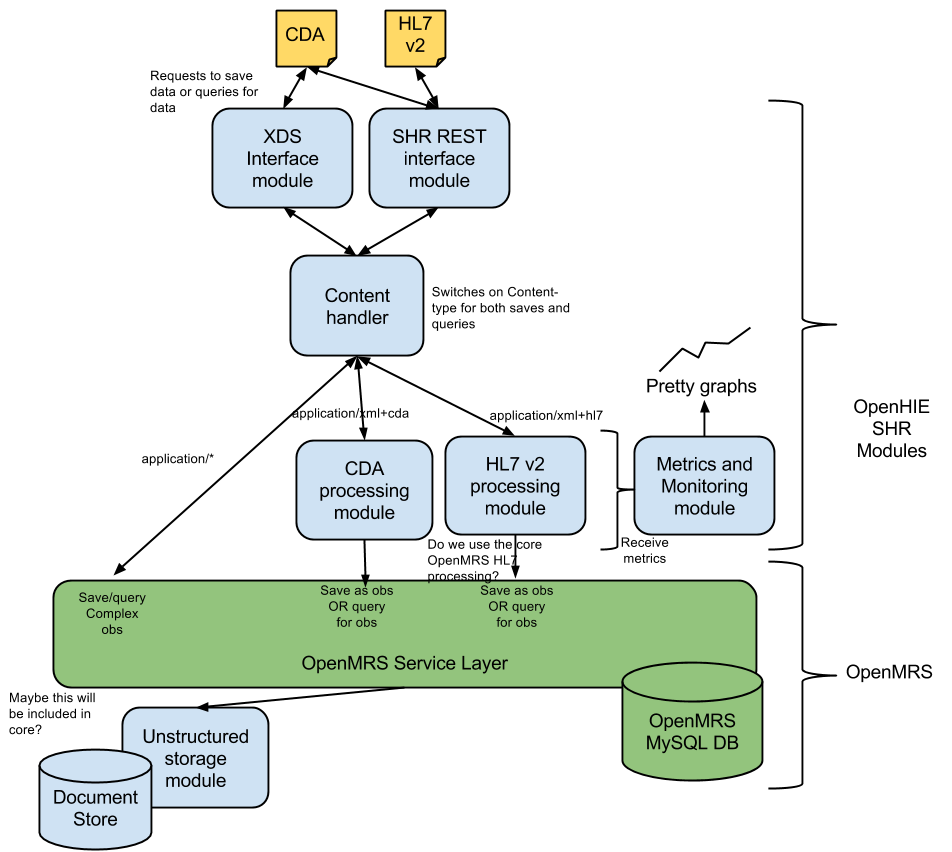
The following diagram describes the overall architecture of the components that would enable OpenMRS to act as a an SHR.
In the initial version of the SHR we would like to be able to revive receive data in 2 different message formats:
- CDA document
- HL7 messages
We acknowledge that we would like to support CDA as the primary exchange format, however, we would also like to support a minimal set of HL7 v2 processing functions to allow legacy applications to send data in this format until such time as they are able to make use of CDA.
...
- The XDS.b IHE profile - this would be the entry point for CDA documents and the primary standards-based interface to receive clinical information.
- A simple REST interface - this would be a simple entry point to receive HL7v2 or CDA documents on.
Basic architecture
The basic architecture for allowing OpenMRS to become a an SHR is to provide a number of modules that expose the interfaces that we need of for the SHR and to allow us to process the message formats data received and store these this in the OpenMRS data model. Also, these module modules must allow data to be retrieved from OpenMRS and formatted in these standardised standardized message formats in the case where data need to be queried by clients.
In order to do this we have require 3 different types of modules:
- Interface modules - these modules provide the service interfaces to send a and receive information using a particular standardised standardized interface.
- Content handler module - this module forwards received data to the appropriate processing module so that it can be stored.
- Processing modules - these modules provide the functionality to interpret data in particular a particular format and store and /retrieve this to/from OpenMRS's data model.
We also consider monitoring as a first-class citizen and a module to monitor how the SHR is performing performance is required. All other module modules are expected to report monitoring data to this module.
Interface Modules
Interface modules provide service interfaces for an external application to call in order to get access to information in the SHR. These modules MUST make use of the content handler module's getContentHandler(String contentType) method (see here) to handle any request to save data or to query data from the SHR.
As part of the default implementation of the SHR, we will implement some specific interface modules. These are described below.
XDS.b interface module
This module provides an XBS.b interface into OpenMRS. It is expected to receive an any type of document payloads over the XDS.b interface and pass those on to the content handler with the content type of the payload.
For the more detailed design of this component see: XDS.b interface module
REST interface module
This module is expected to provide a RESTful interface for receiving and querying HL7 v2 messages as well as CDA documentsCDA documents. In the future, it will conform to a subset of the RESTful FHIR specification which is planned to be used for the future IHE MHD profile once it is stable. It will pass the received data on tot he to the content handler with the content type of the payload. However, for now, these specifications have not been completed and are not releases. As such we will produce a simple REST module in order to test the rest of the SHR architecture until such time as we have proper profiled specifications to develop against.
The design for this basic REST module can be found here: Simple SHR REST interface module
For the more detailed design of the MHD/FHIR module see: FHIR Document interface module (This will be updated as new specifications emerge)
Content Handler Module
This module receives data from the interface handler along with the content type of that data. Using this information it is expected to forward data to the appropriate processing module that can handle that data. It is also required to have the functionality to allow processing module modules to be able to register dynamically register and de-register their interest to data of particular content types dynamically.
For the more detailed design of this component see: Content Handler Module
Processing Modules
Processing modules are able to process data in a particular format to save into OpenMRS and to query OpenMRS for data and convert this to the supported format. Processing modules MUST implement the ContentHandler interface of the content handler module MUST register their content handler with the content handler module to make it available to other modules. See here for more details about the content handler module.
CDA Processing module
The CDA processing module is expected to be able to process CDA documents and store these within OpenMRS's data model. It should also provide functions to retrieve information from OpenMRS and construct this as a CDA document as required.
...
The HL7 v2 processing module is expected to be able to process HL7 v2 message messages and store these within OpenMRS's discrete data model. It should also provide functions to retrieve information from OpenMRS and construct this as a HL7 v2 messages as required.
Unstructured data processing module
OpenMRS's relational database tables will be used to store this information and this can be stored and queried using the normal OpenMRS services.
Alternatives for HL7 V2 message processing
Currently, the RHEA implementation uses the RHEASHRAdapter module for hl7 message generation. Another alternative is the HL7Query module, which was built by OpenMRS developers in response to the use cases and requirements highlighted by the development of the RHEASHRAdapter module. Therefore, the hl7 generation component of the HL7Query module may be used for the second phase of this effort.
More information about HL7 processing concerns is at SHR HL7 processing issues.
The unstructured data storage module
The unstructured data storage module The unstructured data processing module is expected to be able to process an other data that cannot be interpreted by any of the other processing modules. It is expected to be able to strore and retrieve data as-is in blob form. This module is useful for handling unstructured information such as images or pdf's but may be able to store any information that cannot be stored in another mannerstore unstructured data as a Complex Observation or a Complex Note. For a more detailed design see the Unstructured Data Processing Module.
Metric and Monitoring Module
...
In addition to the creation of these modules, there are some changes that we would like to make to OpenMRS itself:
- Remove the requirement to have to store patient names and dob date of birth as we would only want to store a patient identifier for a an SHR
- Performs database modifications to improve performance for SHR functionality
- Add data lifecycle hooks for certain processes to hook into (for example clinical decision support functionality)
- Enable OpenMRS to be able to scale horizontally
Older notes:
Support unstructured data
Due to the need to manage document based (unstructured) data, we are interested in considering alternative methods other than just traditional RBDMS databases for the SHR.
Separate UI from service layer
TODO
Initial ideas:
OpenMRS already exists as two separate maven projects, one containing the view layer and one containing the service layer. Can OpenMRS already be deployed with just the service layer? We will need to check this with the OpenMRS devs.
Add standards-based interfaces
TODO
Initial ideas:
These could be added as modules, one per standard interface supported.
Process and store standards-based data
TODO
Initial ideas:
This logic could be stored in the module alongside the standard-based interface code.
Data lifecycle hooks
TODO
Initial ideas:
We could use hibernate interceptors or AOP to accomplish this.
Make sure everything can be mapped to as encounter-based domain model
TODO
Initial ideas:
TODO
Allow the OpenMRS SHR to scale horizontally
TODO
Initial ideas:
TODO
Modify the database for performance based on the SHR use case
TODO
Initial ideas:
TODO
NOTE :
If you're an OpenMRS developer who is new to OpenHIE, and want a quick refresher, or if if you're interested in reading up on these topics in depth, please refer to OpenMRS as the SHR design document : A quick introduction for OpenMRS developers
- Develop encounter (and possibly obs) attributes as a means of storing additional information such as user-specified identifiers. The need for this is discussed in more detail here.
- Discuss ways to improve Obs table performance (if possible). This should include alternatives other than scaling. Can changing the structure of the table / splitting it up to be of any use to us?
...